13Cubed - Windows Memory Challenge
I was searching for a video to watch while I was eating and then I found this video by 13cubed :D
You can download the memory sample here:https://cdn.13cubed.com/downloads/windows_challenge.zip
First, I launch my very best friends VolWeb and MemProcFS on the FLARE VM :p As we know, the memory sample is from a Windows Machine so we don’t need to build our profile. MemProcFs and VolWeb can download the symbols from the Microsoft’s websites. We just need an Internet connection.
What is the hostname of this device?
After creating the case and uploading the memory dump on VolWeb, we can search through all the volatility plugins. For the computer name, I found it in the envars plugins by searching for COMPUTERNAME.
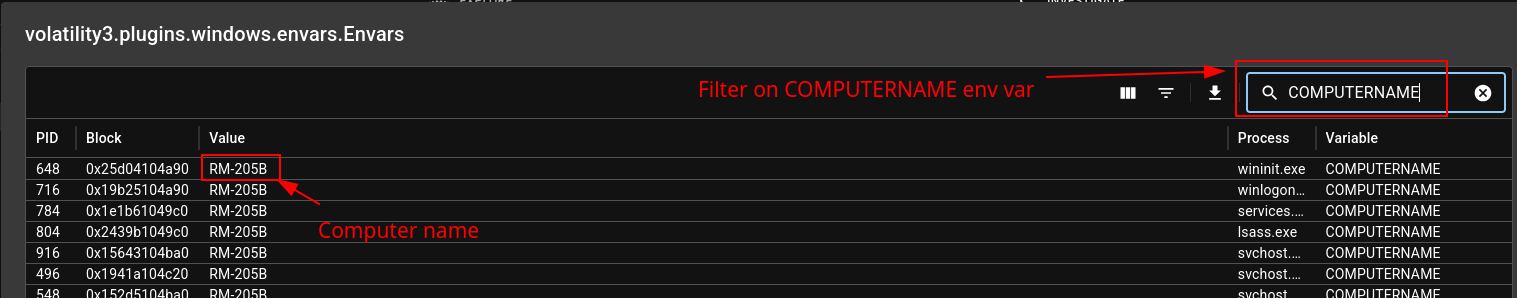
RM-205B
What is the username of the primary user on this device?
For the primary username, I search in the exact same place as the computer name:
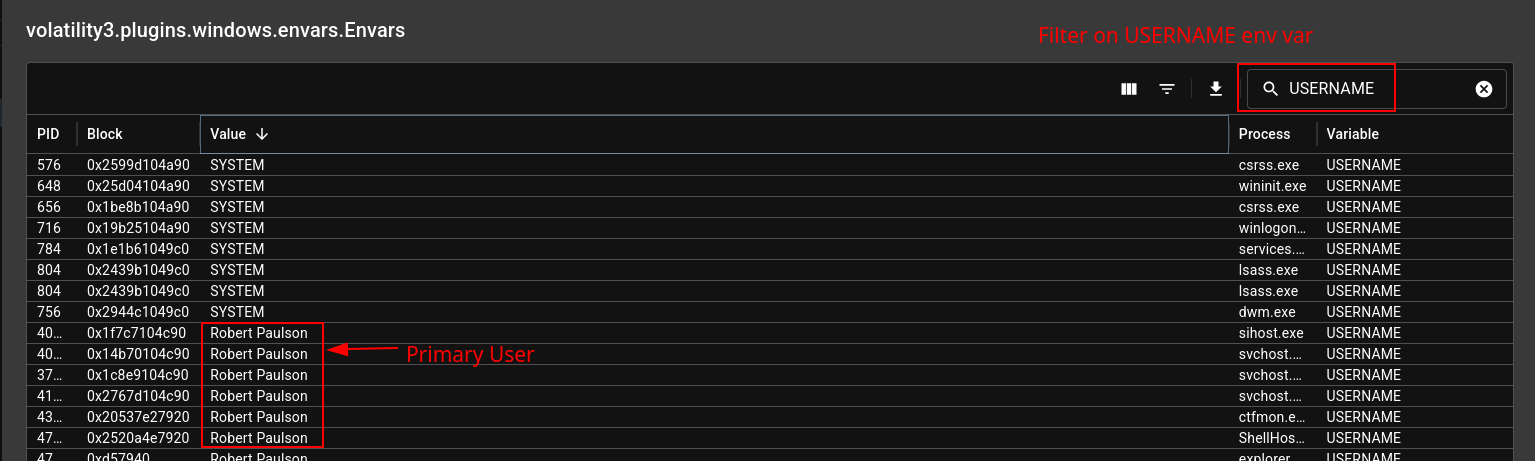
I found the Robert Paulson user who looks like a real user. Look like a Fight Club reference….
Robert Paulson
What is the IP address assigned to this device?
For this question, I launched MemProcFS with this command line: MemProcFS.exe -forensic 1 -device Z:\memory.dmp. After seeing the mounted drive, I looked in the M:\registry\HKLM\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\ and then in the GUID of the interface. All other GUID were unfortunately empty so the right one was easy to find.
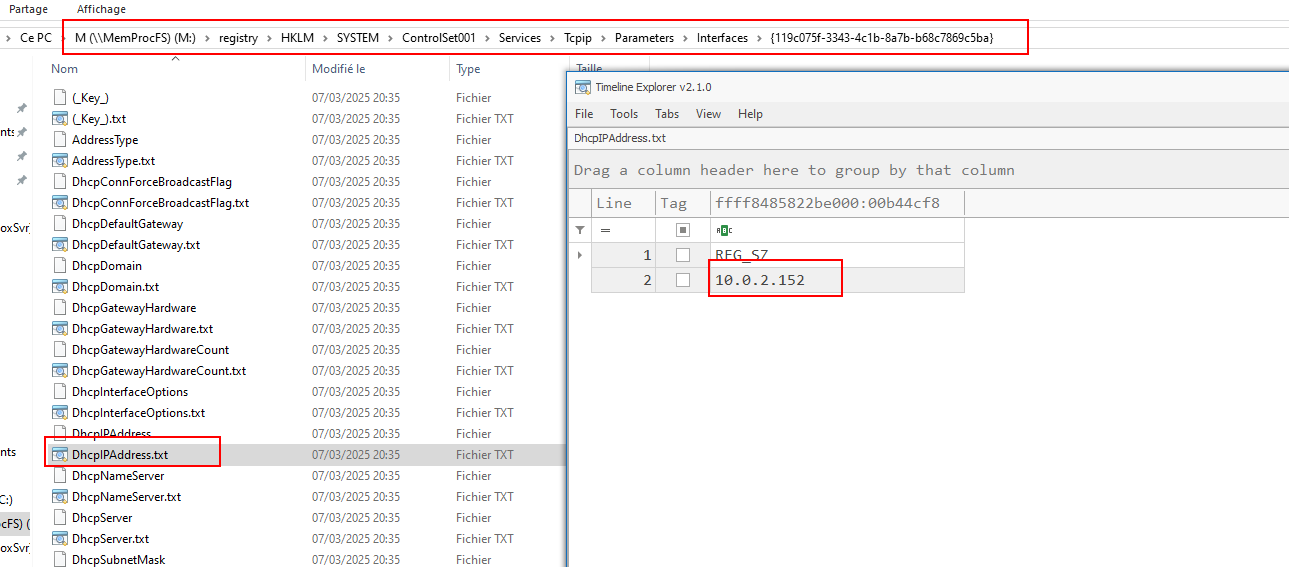
10.0.2.152
What was the full URL, including file name, that the malicious program was downloaded from?
A quick filescan and export it to a txt file:
python3 /opt/volatility3/vol.py -f memory.dmp windows.filescan > filescan.txtNow I can grep on the Downloads directory of the main user:
cat filescan.txt | grep -i "Users\\\\Robert\ Paulson\\\\Downloads"
0xe00921b2fce0 \Users\Robert Paulson\Downloads\desktop.ini
0xe00921e834d0 \Users\Robert Paulson\Downloads
0xe00921e8d2a0 \Users\Robert Paulson\Downloads\backup.exed 400565.crdownload
0xe009225210f0 \Users\Robert Paulson\Downloads
0xe009230b6180 \Users\Robert Paulson\Downloads\backup.exeAs we can see, the backup.exe file have been downloaded from the web following the .crdownload file extension. The crdownload file extension is placeholders for Chrome downloads. Once the download finished, chrome renames the .crdownload to the real filename. Unfortunately, the .crdownload file does not contains that much information:
python3 /opt/volatility3/vol.py -f memory.dmp -o output windows.dumpfiles --virtaddr 0xe00921e8d2a0strings output/file.0xe00921e8d2a0.0xe009251aa980.DataSectionObject.backup.exed\ 400565.crdownload.dat
AnaheimAs we know, the filename is backup.exe, so let’s grepppp:
strings memory.dmp| grep -E '^http://.*backup.exe$'
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe-465e-a769-fde9437ceaccC:\Users\Robert Paulson\Downloads\backup.exeC:\Users\Robert Paulson\Downloads\backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
http://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exehxxp://167.172.227.148:8080/backup.exe
Question 5: According to this execution artifact that would not be found on servers, the first execution occurred within 10 seconds of what time?
“That would not be found on servers” may suggest that this is about the Prefetch artifacts. Unfortunately, Windows Prefetch aren’t enabled by default on Windows Servers, which is not the case for Windows Workstation. Let’s try in MemProcFS:
After founding the Prefetch associated with the backup.exeexecution, I ran PECmd.exe in order to extract all the information.
Unfortunately the Prefetch from MemProcFS does not work :(
Actually, we can cheese this one, let’s check the ntfs_files.txt from MemProcFS:

As we can see, the original backup.exe file has been created the 2025-03-07 at 19:40:36 UTC and the Prefetch file is created the same day at 19:41:08. We can conclude that the first execution generated the BACKUP.EXE-AB6C9DDF.pf file at 19:41:08 UTC.
2025-03-07 19:41:08 UTC
According to the malicious program’s log file, how many files were encrypted?
Usually, whenever a user is infected by a ransomware, there’s indications on what to do next on the computer’s Desktop. Like a Slenderman note or something.
cat filescan.txt | grep -i "Users\\\\Robert\ Paulson\\\\Desktop"
0xe00921b2a880 \Users\Robert Paulson\Desktop\desktop.ini
0xe00921e75240 \Users\Robert Paulson\Desktop
0xe0092510ee50 \Users\Robert Paulson\Desktop\RM-205B-20250307-194124.dmp
0xe0092512a880 \Users\Robert Paulson\Desktop\DumpIt.exe
0xe0092516b0b0 \Users\Robert Paulson\Desktop\DumpIt.exe
0xe00925170830 \Users\Robert Paulson\Desktop\encryption_log.txtPretty interesting file: \Users\Robert Paulson\Desktop\encryption_log.txt
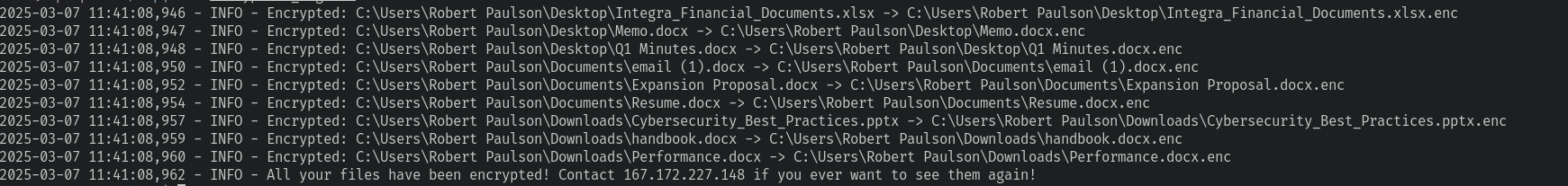
As we can see in the note, there is 9 files that have been encrypted.
9 files were encrypted
What is the NTFS creation time for backup.exe?
Luckily, MemProcFS try to reconstruct the filesystem himself following the NTFS MFT file entry in-memory only (see here). So the $MFT file was not needed because MemProcFS did it for us. Thank you :p
After opening the same text file as in the Question 5, the rows title were empty, but a quick check in the documentation did the job:
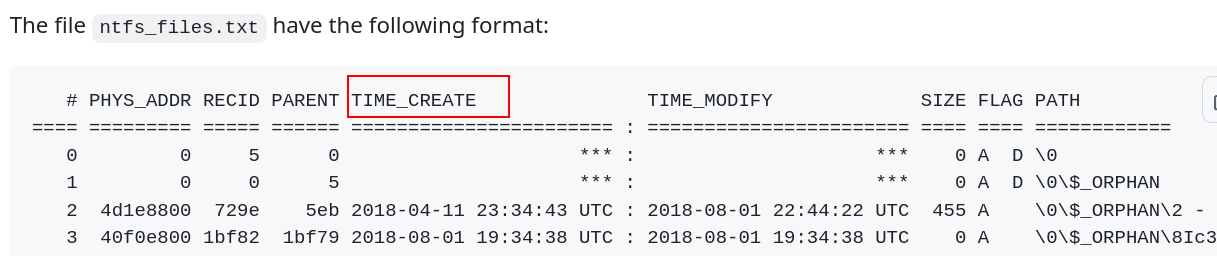
So after lauching the ntfs_files.txt file in TimelineExplorer, we can find the TIME_CREATE field for backup.exe:
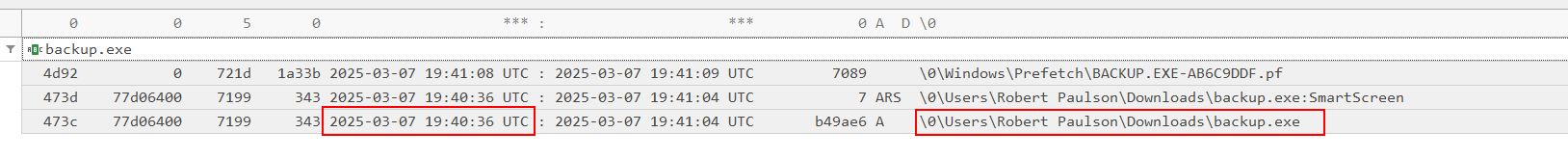
2025-03-07 19:40:36 UTC
What is the full path and name of the public key created by the malicious file?

During my analysis, I saw that the Prefetch file for backup.exe was created at 19:41:08 UTC.

2025-03-07 19:41:08 UTC is the creation time of the Prefetch file. We can assume that the execution of backup.exe is at the almost exact same moment. So let’s see if a key can be found around that time:
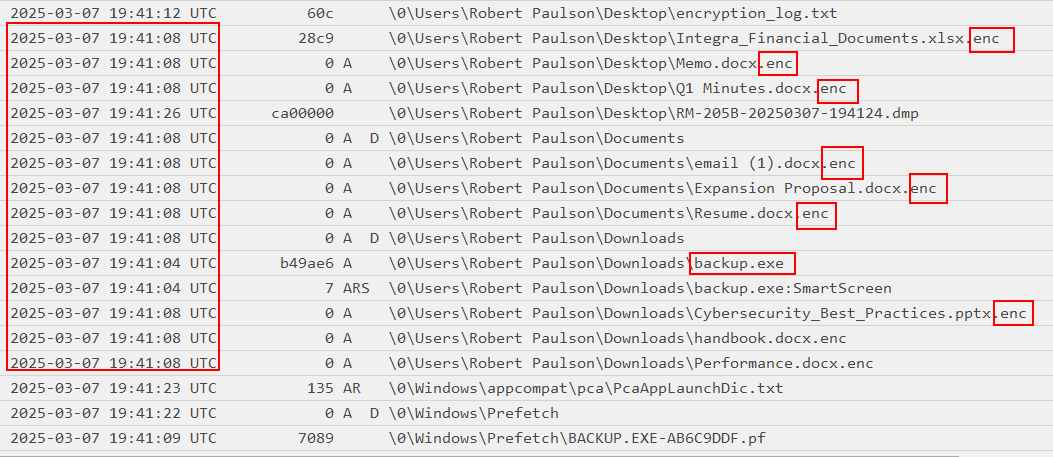
2025-03-07 19:41:08 UTC, the files were encrypted. It can be seen by the .enc extension. Let’s dig if we can see something interesting
At the exact same moment, a file named Users\Robert Paulson\AppData\Local\Temp\tmp98p1q14j is created, kinda suspicious isn’t it?

Let’s see if we have something in the memory dump:
cat filescan.txt| grep -i "tmp98p1q14j"
0xe009230c3470 \Users\ROBERT~1\AppData\Local\Temp\tmp98p1q14jLet’s extract it:
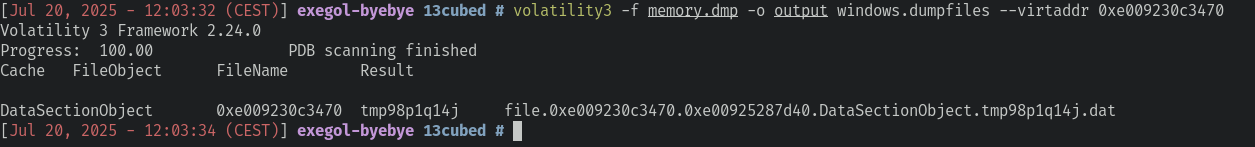
And see if there’s something inside:
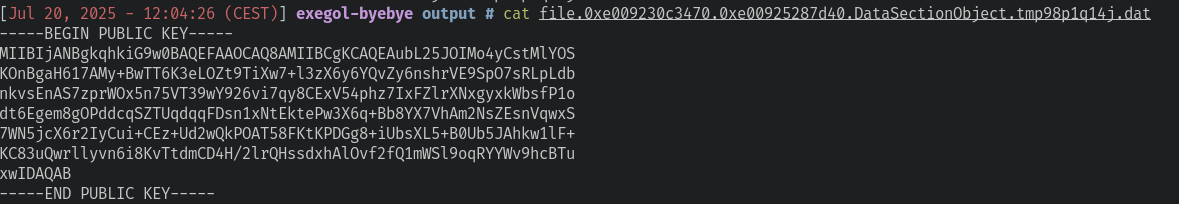
gagné!
The public key: C:\Users\Robert Paulson\AppData\Local\Temp\tmp98p1q14j
What is the first line of key material from the TA’s private key?
This one is a little bit tricky, so let’s start by grepping the common pattern for RSA Private Key:
grep -a 'BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY' memory.dmp -A 60 -B1Result:
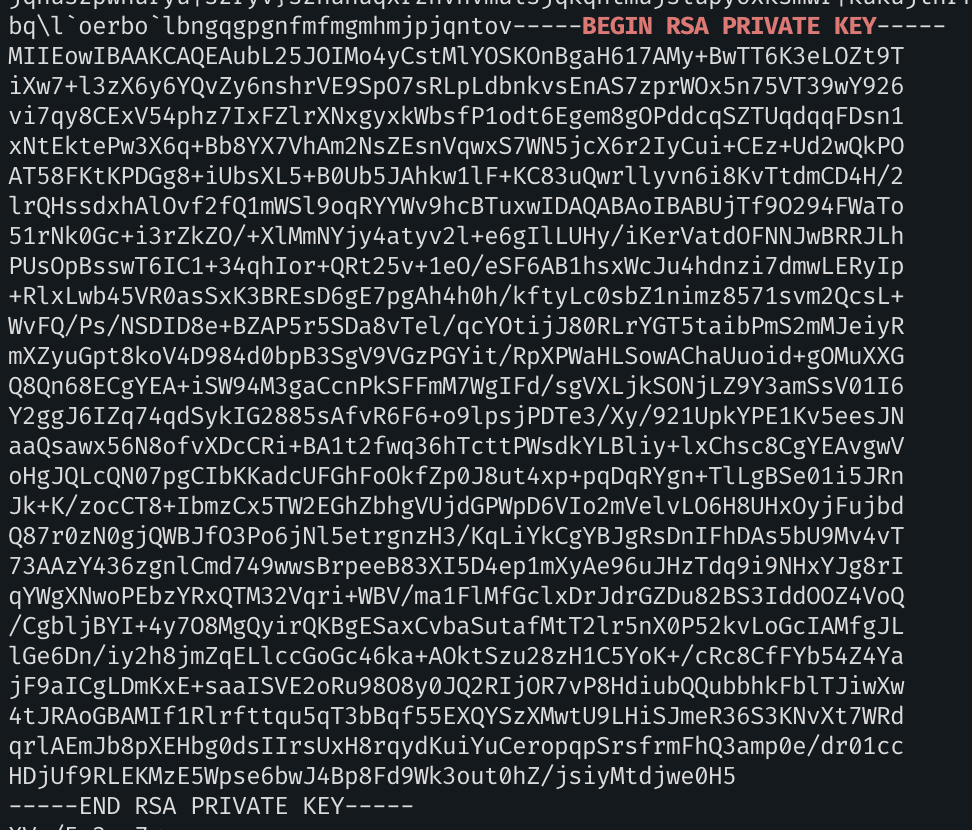
Now we need to check if the private key is linked to the public key we found earlier. For this, export the two keys in two different text files and then:
openssl rsa -in private.key -check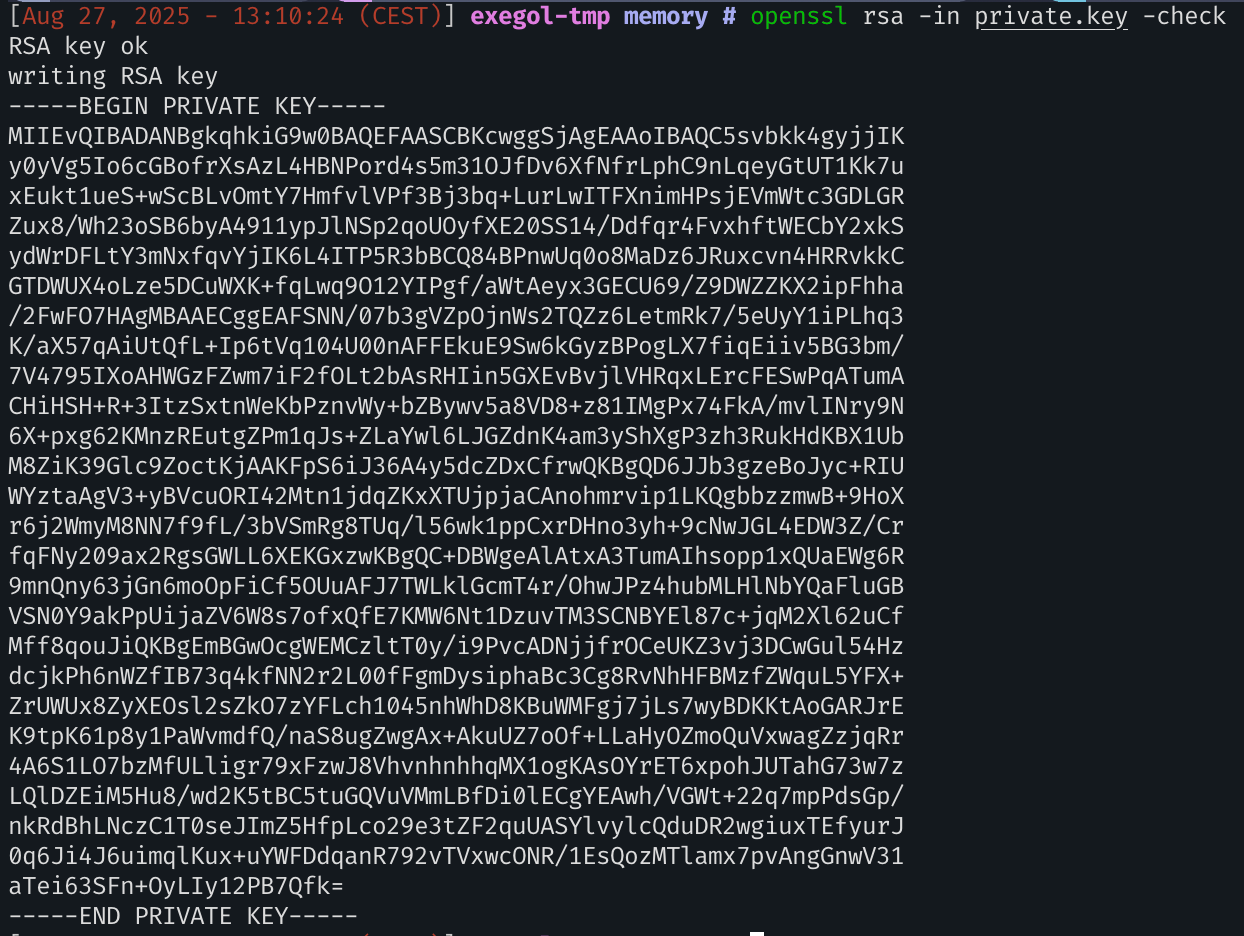
Now it’s time to prove that the two keys are linked. If I can sign a message with the public key and then decrypt it with the private key, it will match! See here for the following commands:
openssl dgst -sha256 -sign private.key -out sig.bin message.txt
# hashes the data, encodes the hash, does type 1 padding and modexp d
openssl dgst -sha256 -verify public.key -signature sig.bin message.txt
# does modexp e and type 1 unpadding, and compares the result to a hash of the data
What is the last web search performed by the user?
For this one, I will dump the History file from the memory using Volatility3:
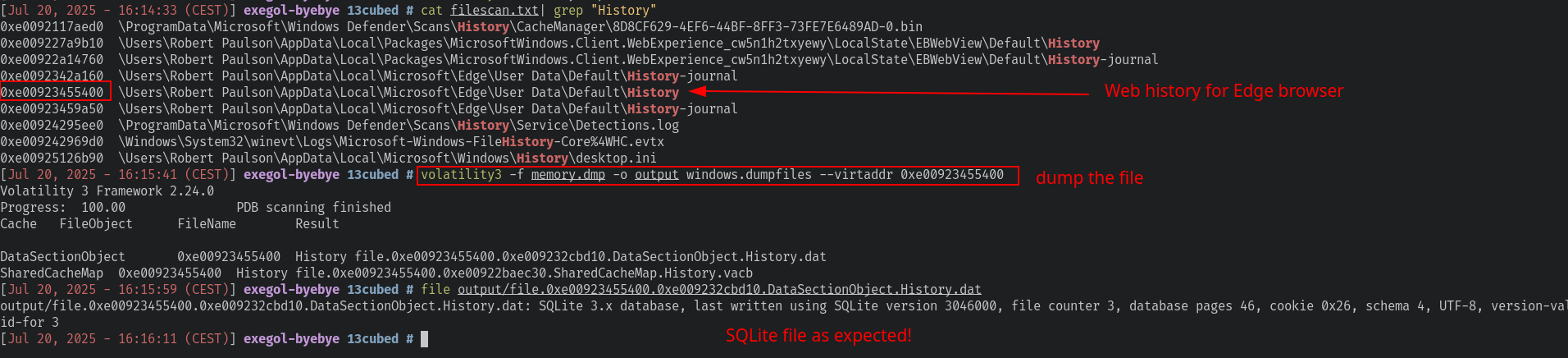
And then we can try to open it in a SQLite browser but we got an errorrrrrrrrrrrr. The file must have been corrupted or not fully extracted in memory. It’s impossible launch it in a SQLite browser.
Let’s cheese. My guess is: The last entry of the file should be the last web research, because it was added at the top of the file. It can be verified by yourself, try to search for something on Edge, the research will be added to the top of the History file. So I opened the file in hexeditor:
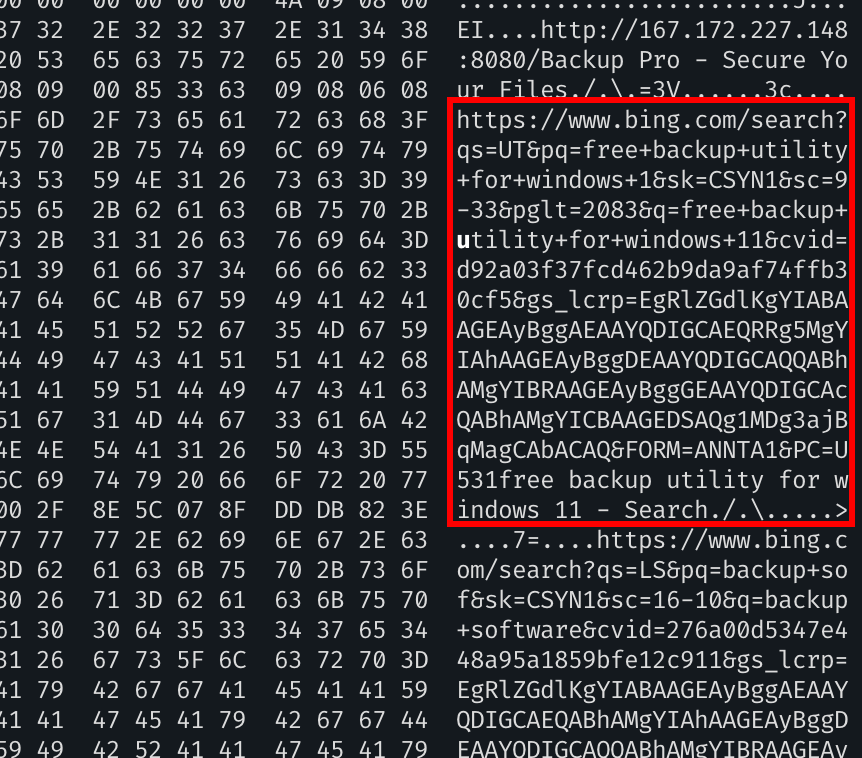
free backup utility for windows 11
What folder does the “Backup Software” landing page tell users to exclude?
As previously seen in the last question, we can see that Robert Paulson clicked on a linked that sent him into “Backup Pro - Secure Your Files”. So let’s grep!
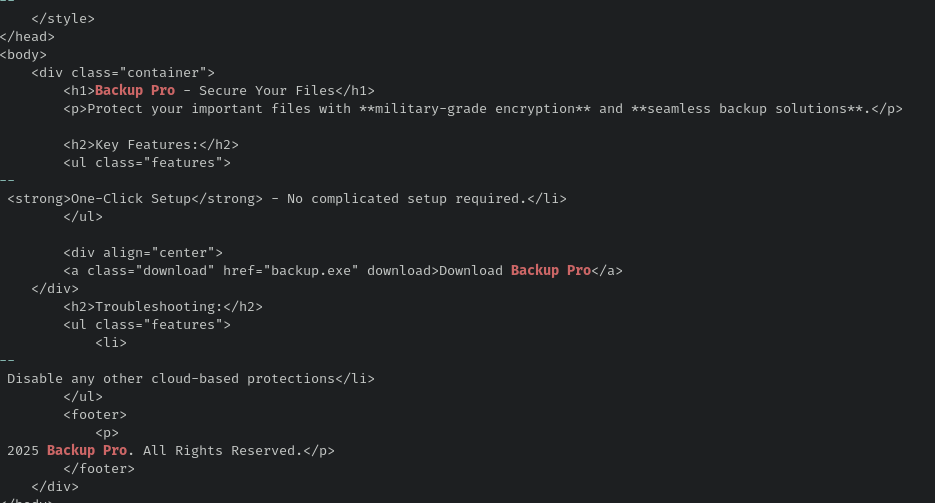
Then I played with strings/grep in order to reconstruct the HTLM file :
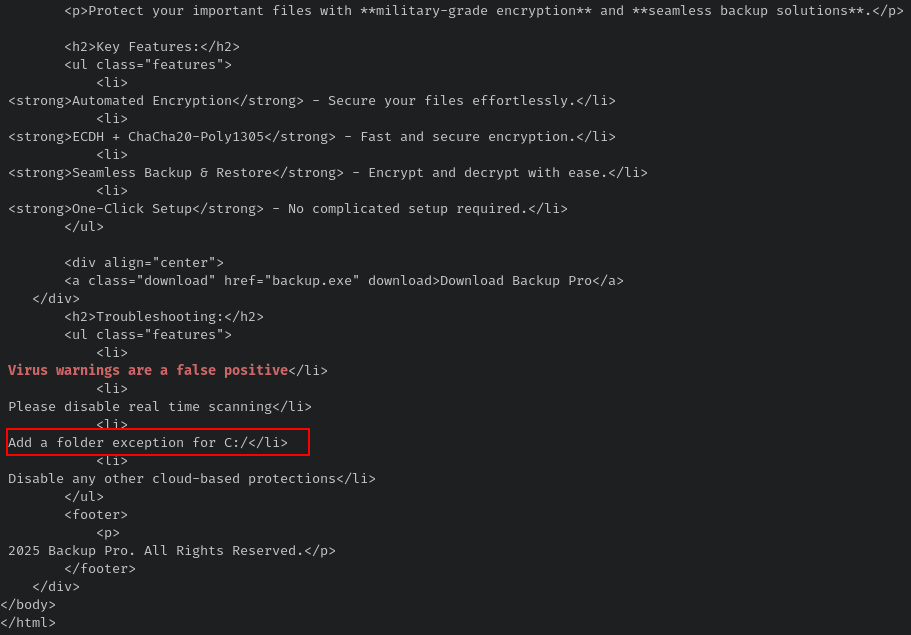
Folder exception: C:\
thank you to 13Cubed for this excellent memory challenge!